Customer Journey Maps: Templates, Examples, and Best Practices

TLDR: Create a customer journey map using our tips, steps, examples, and best practices – then reap the rewards. Also, our AI-powered Customer Journey Map Generator will help you create one in minutes.
So what? Creating and using a customer journey map can help you better serve your customers, creating brand adherents and contributing to a healthy company bottom line.
How to Use Our Customer Journey Map Generator
Our Customer Journey Map Generator creates a pretty good content journey map in just a few minutes. Instead of spending hours planning out all the stages of your ideal customer journey, just answer a few questions and we’ll generate a draft customer journey map, ready to send to your marketing team — instantly and free.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
Think about the last time you bought a new product or service. You went through a journey: researching options or hearing about it, checking out the website or product label, making the decision to purchase, then perhaps becoming a loyal customer.
All customers go through a similar journey of decision-making, information gathering, and (hopefully) delight. This customer journey can be summarized in a customer journey map, which provides a high-level view of all the customer touchpoints that we must think about as marketers. Customer journey maps also provide a way to spot friction points in your customer experience: places to measure and improve.
Stages of the Customer Journey
The customer journey stages below are typical for most industries and customers (though you may need to adjust for your business):
- Awareness/Out of Market: The initial stage where a potential customer becomes aware of your brand, product, or service. This could be through advertisements, word of mouth, social media, or other channels.
- Trigger: Here, the potential customer faces initiating factors that prompt consideration. Usually, this is the first customer touch point.
- Consideration: The customer now takes stock of all available options for purchase. They might look at product reviews, compare options, read blog posts, or watch videos to inform their decision.
- Decision: At this stage, the customer decides what to buy and how much. Businesses must ensure a smooth purchasing process, whether online checkout or in-store experience.
- Post-Purchase: Following the purchase, your company conducts strategic interactions to inquire about satisfaction and to help ensure loyalty. Businesses should provide excellent post-purchase support, ensuring customers are satisfied with their choice.
- Advocacy: Finally, satisfied customers become your brand’s advocates and serve as a potential entry point into the customer journey for another person.
Customer journeys vary from one industry to the next and from one product or service to another.
Marketer’s Takeaway: The customer journey may look like a marketing or sales funnel. In our digital age, however, it’s often the case that different customers may move in and out of this journey multiple times. According to LinkedIn, 95% of customers in the B2B market aren’t “in-market” when they encounter your content–but they will be at some point. This means mapping your journey, so that customers can jump in smoothly at any point.
How to Research Your Customer Journey

Customer journey research generally breaks down into two categories:
Primary Research
Primary research is when your business engages with customers and data directly, getting firsthand the account of customer behavior:
- Customer Interviews: Communicate directly with those who have purchased from you to learn about their experiences and any difficulties they encountered.
- Polls: Gather quantifiable data concerning customer needs and shopping patterns.
- Observation: Watch your customers interact with your brand’s offerings in real time (i.e., in a brick-and-mortar store).
- Data Analysis: Intelligent CMS and marketing platforms provide organizations with analytics and insights on customer behaviors in an increasingly granular fashion.
Secondary Research
Secondary research is the insights and information you can get from the industry itself, typically from outside sources or reporting agencies:
- Studies, Reports, and White Papers: Read what industry experts and those in your industry are saying and have concluded from their research.
- Competitor Research: Look at how your competitors treat customers. What can you learn, what should you avoid, and how do customers feel about their process?
- Social Awareness: Keep a finger on the pulse of online conversations about your company or industry.
Marketer’s Takeaway: Many tools are available to interested businesses seeking insight into their customer journey. However, the (seemingly) most reliable and impactful form of research is digging deep into customer behavior data. This isn’t surprising–Linchpin SEO states that up to 67% of a buyer’s journey will occur in a digital space. CMS and marketing platforms provide incredibly detailed information about nearly any customer behavior you can imagine.
How to Craft A Customer Journey Map
A customer journey map is a logical (and, often, visual) representation of your customer’s experience, from first contact or awareness of your company to long-term loyalty. Creating a customer journey map will provide you with much-needed insight into the needs and wants of your brand’s customers at every stage of their purchasing journey.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
- Define the Objective: Clarify your goals. Do you want to improve a particular aspect of the customer experience or a holistic view of the entire journey?
- Leverage Customer Personas: Develop a thorough understanding of your target audience’s needs. In most businesses, there might be multiple customer personas, each with unique journeys.
- List Touchpoints: Identify every opportunity for interaction between your brand and the consumer. This can include your website, social media channels, in-store experience, customer service, and emails.
- Visualize the Journey: Map out your customer’s progression through every stage. Use the classic stages of the customer journey: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, Advocacy.
- Highlight Pain Points: Find areas where customers are challenged or dissatisfied in their journeys. Be sure to call on rational customer decision-making and potential emotional connections that your brand can make with the customer.
- Iterate: Continuously update and improve the map based on feedback and evolving customer behaviors.
Tools for Journey Mapping:
Consider some of the following platforms for help in mapping:
- Media Shower’s Customer Journey Map Templates (+Examples and Prompts)
- HubSpot’s Free Customer Journey Map Template
- UXPressia’s Online Customer Journey Mapping Tool
- LucidChart Customer Journey Mapping Software
Marketer’s Takeaway: There are several ways to conceptualize a customer’s journey, whether visual or otherwise. Visual artifacts can provide a clear, big-picture view of this journey… but if you find yourself fiddling with diagramming technology rather than focusing on the meat of that journey, it’s completely productive to use normal words and ideas to describe it. Likewise, many marketers are turning to generative AI to help them start sketching the broad strokes of their customers’ journeys.
Customer Journey Map Examples
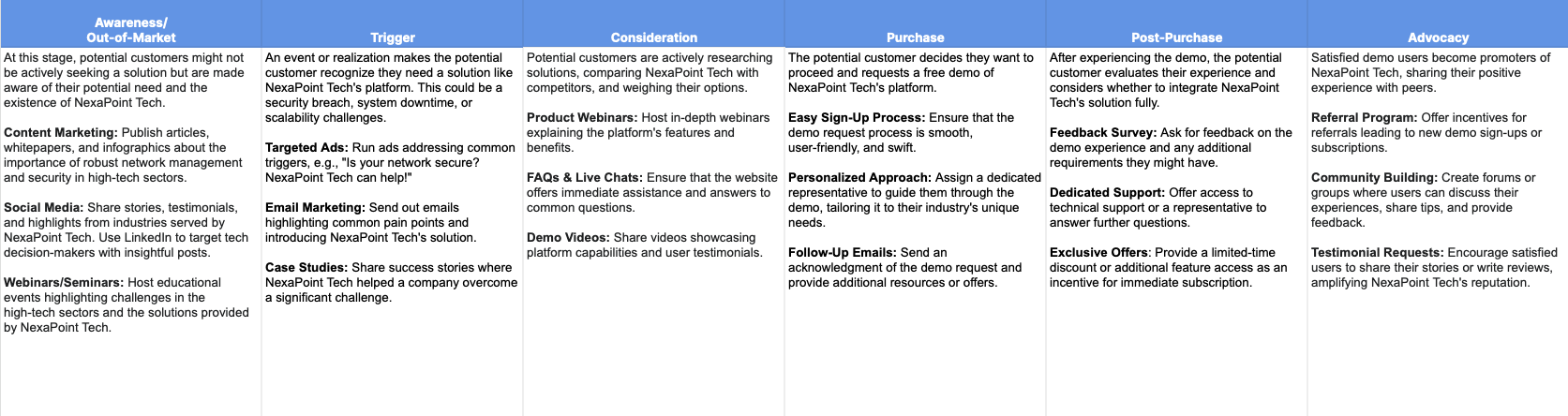
Example 1: NexaPoint Tech
This customer journey represents the fictional brand NexaPoint Tech. This network-management SaaS platform wants to develop a journey for customers to move towards their free demo. The journey covers the stages we’ve outlined in this article. It provides several assets and techniques to ensure that the customer is always delivered with what they need to take the necessary next action.
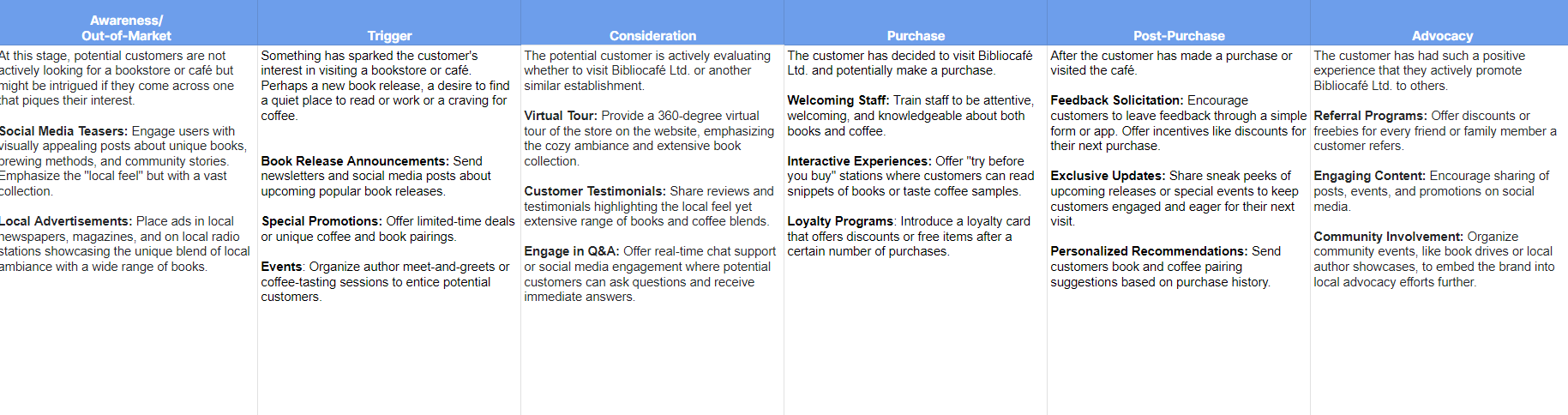
Example 2: Bibliocafe
This customer journey is for the fictional brand Bibliocafe. It operates brick-and-mortar stores that tailor their appearance and layouts to local cultures and customs while providing the robust customer support one would expect from a major chain bookseller. This customer journey demonstrates how to usher someone from not knowing about the brand to physically entering the store and making a purchase.
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices

Crafting an effective customer journey map requires a strategic approach. You also need a focus on customer perspectives, collaboration, and flexibility.
Some best practices for mapping and improving your customers’ journeys:
- Customer-Centric Perspective: Start by focusing on the consumer’s perspective rather than your or the larger company’s internal processes.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Make sure you have a comprehensive journey map by encouraging collaboration across company departments.
- Regular Updates: Keep your journey maps dynamic by regularly updating them to align with changing customer preferences.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Identifying and addressing pain points and bottlenecks in your customers’ journey will boost customer satisfaction.
- Technology and Analytics: Leverage technology and data analytics for real-time monitoring and customization.
- Consistency Across Touchpoints: Maintain a consistent brand experience by maintaining cohesion across customer interactions.
- Continuous Customer Feedback: Encourage customers to leave feedback at every journey stage. This will promote continuous improvement in the process.
- Define Breadth and Goals: Outline the scope of the journey you’re seeking to map and your goals in doing so.
- Pinpoint Customer Personas: Understand and define distinct customer personas and their journeys.
- Gather Data: Gather relevant information and data points on customer interactions with the company to inform the mapping process.
- Use Visual Representation: Create a visual representation of the customer journey to enhance your company’s understanding of what’s happening.
- Validate and Refine: Check and distill the map through internal and external feedback to ensure your creation is accurate and relevant.
- Implement, Then Monitor: Implement the insights gained from the customer journey mapping, then monitor the improvements made to keep improving the customer experience.
Work with Media Shower to Craft Your Next Customer Journey Experience
Mapping the best customer journey is an art. Still, it is a dynamic and continual process that should reflect changing consumer preferences. As a marketer, you want to keep the customer in mind when making business decisions, and recognizing the pivotal role your customers’ experiences play can help you shape brand loyalty.
By creating a new customer journey map (or refining an existing one), your company can foster a customer-centric approach that will contribute to the growth of your business.
___________
Need help crafting your customer journey map? We’ll be your guide. Take Media Shower for a test drive today.


